BIOS Settings Guide for Dell, HP, and Lenovo | Easy and Clear Explanation
When you turn on your computer, something important happens before Windows appears. A small program wakes up all the computer parts, checks that everything is working, and then starts the operating system. This small program is called the BIOS.
Many people feel nervous when they hear the word “BIOS” because it sounds technical. But the truth is simple: BIOS is just the “starter” of your computer.
In this guide, you will learn what BIOS is, why you may need it, and how to use it safely on Dell, HP, and Lenovo devices. Everything is written in clear, easy words.
1. What Is BIOS?
BIOS stands for Basic Input/Output System.
You don’t need to remember the long name. Think of BIOS as the “morning alarm” for your computer. When you press the power button, BIOS wakes up and checks:
- Is the keyboard working?
- Is the screen showing properly?
- Is the RAM okay?
- Is the storage device (SSD or HDD) connected?
Only after these checks does the BIOS allow Windows to start. So, the BIOS works even before the Windows logo appears.
Read Also: Why Computer is so Powerful?
2. Why Do People Open the BIOS?
Most of the time, you never need to open the BIOS. But in some situations, it becomes useful. For example:
- If you want to install Windows from a USB
- If you need to turn on Virtualization for a program
- If your computer is not starting properly
- If you need to enable Secure Boot or TPM for Windows 11
- If you want to reset everything to default
- If you need to update the BIOS for better performance
These tasks sound complex, but they are simple when explained properly.
3. Important Safety Tips Before Changing BIOS Settings
BIOS is powerful, so you must be careful. Follow these rules:
- Do not change options you don’t understand.
- Make sure your laptop has enough battery or stay plugged in.
- Never turn off the computer during a BIOS update.
- Take pictures of your current settings before changing anything.
- If something goes wrong, use the “Reset to Default” option.
If you follow these tips, you won’t face any problems.
Read Also: How to Tell if Your Computer Has a Virus?
4. How to Enter BIOS on Dell, HP, and Lenovo

Every brand uses special keys to open the BIOS menu. You must press these keys right after turning on the system.
Dell
Most Dell systems use:
- F2 for BIOS
- F12 for Boot Menu
Turn on your computer and tap F2 repeatedly until the BIOS screen appears. If it doesn’t work, try F12.
HP
Most HP devices use:
- Esc for Startup Menu
- F10 for BIOS
Turn on the laptop, tap Esc, then choose F10 from the menu.
Lenovo
Lenovo laptops have two methods:
Method 1: BIOS Keys
Tap F1 or F2 quickly after turning on.
Method 2: Novo Button
Some models have a small button beside the power button. Press this button with a pin while the device is off, and choose BIOS Setup.
This works even if the keyboard is not responding.
5. Understanding the BIOS Menu (Easy Explanation)
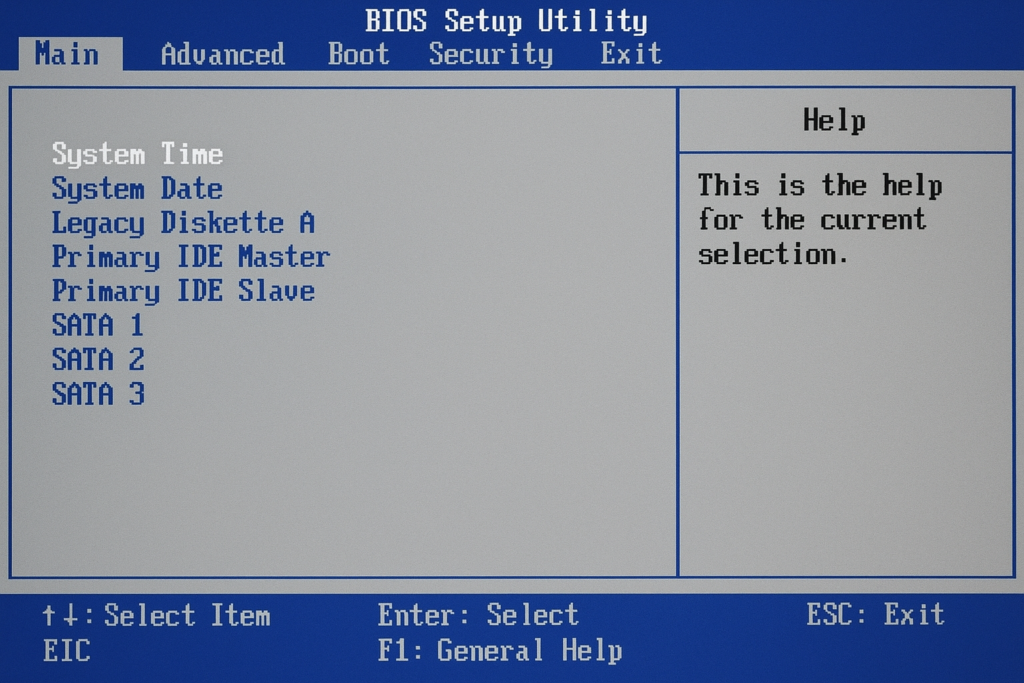
When BIOS opens, you will see several sections. They may look confusing at first, but here’s what they mean in simple language:
System Information
The System Information page shows basic details about your computer. You can see the processor, RAM, storage type, and the current BIOS version.
This page is only for viewing information. You cannot make any changes here. It helps you understand what hardware your computer has.
Boot Settings
Boot Settings determine where your computer starts from when you turn it on. Usually, it starts from the internal hard drive. You can also select a USB drive or DVD if you want to install Windows or run a recovery tool. Changing the boot order can help fix startup problems.
Security
The Security section contains options like Secure Boot, TPM, and BIOS passwords. These features help protect your computer from viruses and unauthorized access.
You can enable or disable some security settings depending on your needs. Most users only need to check that Secure Boot and TPM are on.
Virtualization
Virtualization allows your computer to run virtual machines or Android emulators. Programs like VirtualBox, VMware, or BlueStacks need this feature to work properly. It is usually off by default, so you may need to enable it if your software requires it. Turning it on is safe for normal use.
Device Configuration
Device Configuration lets you control hardware features such as the camera, touchpad, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and USB ports. You can enable or disable these devices depending on what you need. This section is helpful if you want to save power or secure your system.
Advanced Settings
Advanced Settings include options for fan control, CPU features, and power management. These options are usually for experienced users.
Changing the wrong settings here can cause problems, so beginners should avoid this section unless instructed. It allows fine-tuning for performance and cooling.
6. Important BIOS Settings You Will Actually Use
You do not need to know everything in the BIOS. Only a few settings matter for everyday users.
Boot Order
This is the most common setting people use.
If you want to install Windows from a USB drive, you must move “USB” to the top of the boot list. After the installation, you can set it back.
Secure Boot
Secure Boot protects your system from harmful programs during startup.
- Keep it ON for normal use.
- Turn it OFF only when installing Linux or certain tools.
TPM (Trusted Platform Module)
Windows 11 requires TPM 2.0.
If your computer says TPM is missing, you can find it in the Security menu and enable it.
Virtualization (VT-X / SVM)
Many apps need Virtualization:
- Android emulators
- VirtualBox / VMware
- WSL2
You can enable it from the Advanced or Security section.
Fan and Cooling Settings
Some Dell and Lenovo models allow you to choose:
- Performance cooling
- Quiet mode
- Balanced mode
This changes how loud or cool your laptop becomes.
Function Key Behavior
Some people want F1–F12 to work normally. Others want them to control brightness and volume.
You can switch this behavior on Dell, HP, and Lenovo systems inside the BIOS.
7. Special Features in Dell, HP, and Lenovo BIOS

Each brand of computer offers unique BIOS features that can help you manage performance, security, and hardware. While the main BIOS functions are similar across brands, these special options give extra control to users who need it.
Dell
Dell BIOS often includes features like fan speed control, which allows you to adjust how your laptop cools itself. It also has RAID settings for advanced storage management.
Many Dell systems include diagnostic tools to check hardware and fast boot options to start Windows quickly. These features are useful for both performance and troubleshooting.
HP
HP BIOS offers options like HP Sure Start, which can automatically repair the BIOS if it becomes corrupted. You can also control touchscreen functionality and adjust the fan for quiet operation.
HP BIOS is designed to be secure and simple, giving users easy control over key hardware features without being overwhelming.
Lenovo
Lenovo ThinkPads include deeper options for power management and hardware security. You can control the fingerprint reader, enable or disable the camera shutter, and access advanced menus for system settings.
Lenovo laptops also have the Novo Button, which provides easy access to BIOS even if the keyboard is not working. These features make Lenovo BIOS flexible and user-friendly.
8. How to Reset BIOS to Default
If you change something by mistake, you can easily reset everything:
- Enter BIOS.
- Look for “Load Defaults,” “Setup Defaults,” or “Reset Settings.”
- Confirm the action.
- Save and exit.
Your BIOS will return to safe, factory settings.
9. Common BIOS Problems and Simple Fixes

BIOS key not working
Try tapping the key faster. Try another key. On Lenovo, use the Novo Button.
Stuck on BIOS screen
This usually means the computer cannot find Windows. Check the boot order, reset settings, or make sure the SSD is detected.
USB not showing for boot
Format the USB as FAT32, recreate the bootable USB, or turn off Secure Boot temporarily.
Greyed-out settings
Your system might have a BIOS password or company restrictions.
Windows not starting after change
Reset BIOS to default or switch storage mode back to original (AHCI or RAID).
10. Updating BIOS Safely
A BIOS update can fix bugs, improve performance, and increase security. But you must update carefully:
- Keep the laptop plugged in
- Use only the official website or official tools
- Do not turn off the laptop during update
Each brand has its own update tools:
- Dell: SupportAssist or Dell Support website
- HP: HP Support Assistant
- Lenovo: Lenovo Vantage or Lenovo Support website
FAQs
1. What is BIOS?
BIOS is a small program inside your computer that helps it start. It checks the hardware and then loads Windows or any other operating system.
2. How do I open BIOS on Dell, HP, or Lenovo computers?
- Dell: Press F2 when the Dell logo appears.
- HP: Press Esc, then press F10.
- Lenovo: Press F1 or F2, or use the Novo button if your model has it.
3. What can I safely change inside BIOS?
You can safely change settings like boot order, Virtualization (VT-x), fan settings, and date/time. These do not harm your computer.
4. What should I NOT change in BIOS?
Avoid changing CPU power settings, voltages, and advanced security chips because wrong settings may stop your system from starting.
5. What is Boot Order?
Boot Order tells your computer where to look first to start Windows. For example: hard drive → USB → DVD.
6. How do I reset BIOS to default settings if something goes wrong?
Inside BIOS, there is always an option like “Load Defaults” or “Restore Factory Settings.”
Click it to fix any wrong changes.
7. What is Secure Boot?
Secure Boot protects your system from harmful programs that try to load before Windows. It is best to keep Secure Boot ON.
8. What is Virtualization?
Virtualization (VT-x) allows your PC to run virtual machines or Android emulators. Many apps like BlueStacks need this setting turned ON.
9. Can BIOS changes damage my computer?
Safe settings will not damage your PC, but changing advanced hardware controls can cause problems. So only change what you understand.
10. Should I update my BIOS?
Yes, but only when the brand (Dell, HP, Lenovo) recommends it.
Download updates from the official website and keep your laptop charged during the update.
Final Thoughts
BIOS might seem scary at first, but it is actually very simple. It is a small program that starts your computer, checks that everything is working, and then opens Windows. With this guide, you can safely open BIOS, look around, and change the settings you need.
For most people, the settings that matter are Boot Order, Secure Boot, TPM, Virtualization, and basic device controls like turning Bluetooth or the camera on and off. You should avoid changing advanced options unless you really understand them. Taking pictures of your current settings can help you return to them if needed.
Dell, HP, and Lenovo computers may look different inside BIOS, but the main features are the same. This guide helps you use any of these brands confidently, fix common problems, and make simple adjustments safely.The most important thing is to be patient and careful. Take your time, read each option, and remember that if something goes wrong, the Reset to Default option can fix it. Now you can handle BIOS without worry or confusion.